Grid Computing
Grid computing is the practice of leveraging multiple computers, often geographically distributed but connected by networks, to work together to accomplish joint tasks. It is typically run on a “data grid,” a set of computers that directly interact with each other to coordinate jobs.
How Does Grid Computing Work?
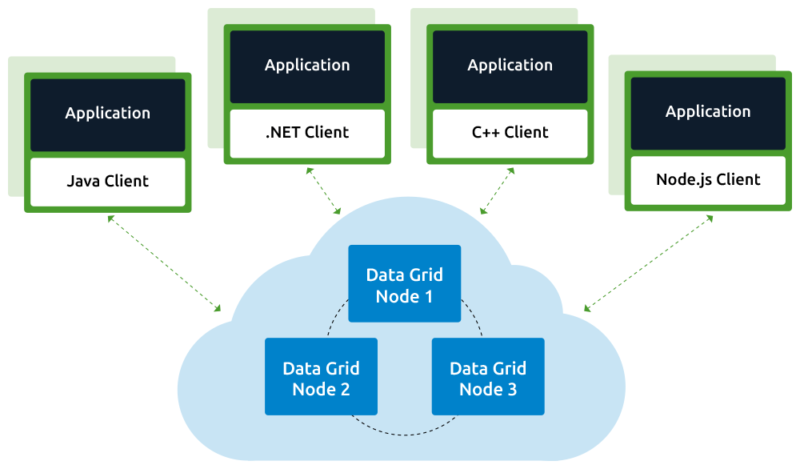
Grid computing works by running specialized software on every computer that participates in the data grid. The software acts as the manager of the entire system and coordinates various tasks across the grid. Specifically, the software assigns subtasks to each computer so they can work simultaneously on their respective subtasks. After the completion of subtasks, the outputs are gathered and aggregated to complete a larger-scale task. The software lets each computer communicate over the network with the other computers so they can share information on what portion of the subtasks each computer is running, and how to consolidate and deliver outputs.
How is Grid Computing Used?
Grid computing is especially useful when different subject matter experts need to collaborate on a project but do not necessarily have the means to immediately share data and computing resources in a single site. By joining forces despite the geographical distance, the distributed teams are able to leverage their own resources that contribute to a bigger effort. This means that all computing resources do not have to work on the same specific task, but can work on sub-tasks that collectively make up the end goal. For example, a research team might analyze weather patterns in the North Atlantic region, while another team analyzes the south Atlantic region, and both results can be combined to deliver a complete picture of Atlantic weather patterns.
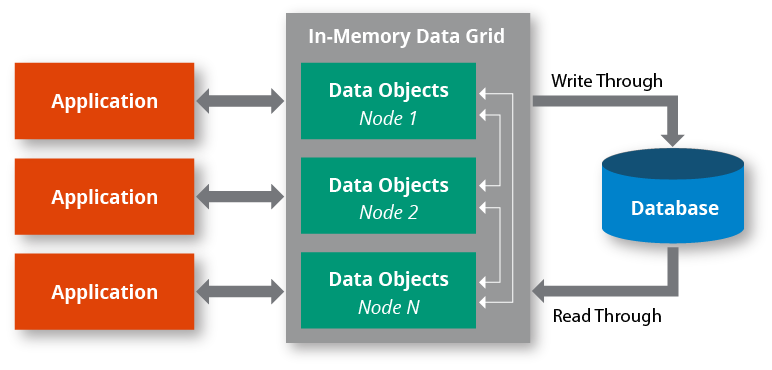
While often seen as a large-scale distributed computing endeavor, grid computing can also be leveraged at a local level. For example, a corporation that allocates a set of computer nodes running in a cluster to jointly perform a given task is a simple example of grid computing in action. A specific type of local data grid is an in-memory data grid (IMDG) in which computers are tightly connected via coordination software and a network connection to collectively process data in memory. The advantage is that the data is stored in memory across all computers in the data grid, so all data accesses are very fast. IMDGs like Hazelcast IMDG are especially useful when the grid computing tasks require extremely high throughput and extremely low latency.